In the design of high-rise buildings, planning the elevator system to ensure both efficiency and the ability to carry a large number of passengers has always been a complex issue.
Reasonable planning of high-rise elevators can not only improve the operating efficiency of the building but also enhance the comfort and satisfaction of users.
This article will provide you with practical high-rise elevator design tips to ensure that your elevator system is efficient, safe, energy-saving, and meets transportation needs.
Key Issues to Consider When Planning High-Rise Elevators
How to Use the Elevator Shaft Space Efficiently
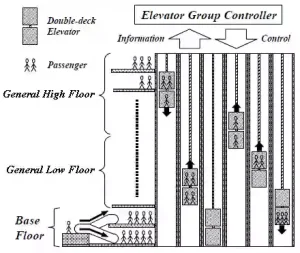
The elevator shaft in a high-rise building occupies considerable space, so effective planning of the elevator core area is key to optimizing building design. Through innovative designs, multi-group elevators, double-deck elevators, and ropeless elevator systems can significantly reduce the space occupied by elevator shafts.
-
Multi-group elevator design: Avoid clustering all elevator systems in one area; instead, distribute elevator groups to improve space utilization.
-
Double-deck elevators: Each group of elevators serves two floors, increasing capacity and reducing the number of shafts.
-
Ropeless elevators: These elevators do not rely on traditional cables, reducing shaft space requirements and adapting to high-rise buildings.
Reasonable Configuration of Elevators to Improve Efficiency
The elevator configuration of high-rise buildings should be optimized based on the building’s actual needs. For example, multi-axis elevators and shuttle elevator systems can make elevator services more flexible and efficient.
-
Multi-axis elevator configuration: Multiple elevators are configured on the same axis to provide multi-directional service, improving transportation efficiency.
-
Shuttle elevator system: Suitable for high-frequency, high-traffic buildings, quickly connecting different floors and reducing waiting time.
How to Optimize Elevator Dispatching Through Passenger Flow Analysis
By analyzing passenger flow in each area of the building—especially peak-hour demand—the elevator dispatch system can be optimized, reducing waiting times and improving overall efficiency.
-
Traffic simulation analysis: Predict passenger flow in different areas through data analysis and adjust elevator dispatch and allocation.
-
Destination control system: Optimize elevator dispatch by directing passengers to elevators based on their destination floor, avoiding unnecessary stops.
How Energy-saving Elevator Systems Reduce Operating Costs
As green building concepts become more prevalent, energy-saving has become a key consideration in high-rise elevator design. Technologies such as energy recovery, intelligent dispatching, and machine room-less elevators can significantly reduce energy consumption.
-
Energy recovery system: Recovers excess energy when the elevator descends to reduce overall energy consumption.
-
Intelligent dispatching system: Optimizes elevator dispatch based on real-time data, reducing unnecessary empty car operation and improving energy efficiency.
Ensure the Safety and Emergency Response Capabilities of the Elevator System
The elevator system design in high-rise buildings must account for safety during emergencies. Fire elevators and emergency backup power supplies are critical to ensuring safe evacuation during fires or other disasters.
-
Destination control system: Ensures that the elevator can respond efficiently in emergencies and evacuate people quickly.
-
Fire elevator design: Ensures there is a dedicated elevator for emergency personnel evacuation that meets fire safety standards.
Tips to Improve the Efficiency of High-Rise Elevators
How to Optimize Elevator Capacity According to Building Needs
Choose the appropriate elevator capacity and number based on the building’s use (e.g., residential, commercial, office). Technologies such as double-decker elevators and multiple elevators per shaft can effectively improve transportation capacity and reduce waiting and parking time.
Choose the Right Elevator Speed to Improve Efficiency
Select high-speed elevators and direct elevator systems for high-rise buildings to minimize waiting and travel times. Especially in high-rise buildings, ropeless and double-decker elevators can significantly improve transportation efficiency.
Design with Future Floor Expansion Needs in Mind
When designing high-rise elevators, it’s important to consider future floor expansions or building renovations. Choosing scalable elevator systems (such as ropeless elevators) ensures the system can meet higher demands in the future.
Application of Intelligent Elevator Control Systems
Implementing destination control and intelligent dispatching systems optimizes elevator operation, reduces stop time, and improves elevator transportation efficiency—particularly in high-rise buildings with heavy passenger flow.
Accessible Elevator Design
Ensure that elevator designs meet accessibility requirements, allowing all passengers—including those with limited mobility—to use the elevator easily. Modern technologies (e.g., seismic sensors and real-time monitoring) should also be integrated to further enhance elevator safety.
High-Rise Elevator Design Planning Process
After understanding the key points and techniques of high-rise elevator design, let’s explore the planning process to ensure that we can complete the high-rise elevator design task efficiently.
1. Preliminary Research and Demand Analysis
Building Function Analysis
Determine the purpose of the building (e.g., residential, office, commercial complex) and the target user group, then assess the elevator requirements. For example, the elevator needs in high-rise residential buildings and office buildings will differ.
Peak Traffic Flow Forecast
Conduct a traffic analysis, calculate the expected passenger flow on various floors, and evaluate the required number of elevators and their speed to accommodate peak traffic.
Space Planning Requirements
Define the space needed for the high-rise elevators, including shaft location, machine room space, backup power supply, and safety equipment.
2. Elevator System Type and Layout Design
High-Rise Elevator Type Selection
Choose the appropriate elevator type for high-rise buildings, considering options like traditional elevators, double-decker elevators, ropeless elevators, etc., based on the building’s height, function, and passenger needs.
Elevator Distribution and Layout
Determine the location of the elevator group. Avoid clustering all elevators in one area. A dispersed layout helps optimize space utilization and reduce waiting times.
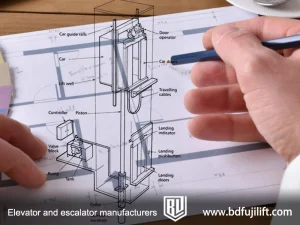
High-Rise Elevator Shaft Design
Calculate the size, number, and coordination of the elevator shafts with the building structure. Ensure that the shaft design meets the building’s load-bearing requirements and facilitates future maintenance.
3. Coordinated Design of the Core Area and Elevator Shaft
Core Area and Vertical Transportation
Ensure the elevator shaft and other parts of the building core area (e.g., stairs, pipe shafts) are efficiently laid out to minimize the core area footprint while meeting functional building requirements.
Coordination Between Shaft and Building Structure
Ensure proper coordination between the elevator shaft and building structure to prevent conflicts with other functional areas (e.g., electrical pipelines, fire protection systems).
4. Mechanical and Control System Design
Elevator Drive System
Select a suitable elevator drive system (e.g., hydraulic, traction drive, ropeless elevator) based on the building’s height and load requirements.
Dispatching and Control System Design
Design an elevator dispatching system that matches the building’s scale to ensure efficient elevator dispatch during peak hours and prevent elevator overcrowding.
Elevator Safety and Emergency Response System
Arrange for safety equipment in the elevator system, including emergency stop devices, battery backup systems, etc., to ensure stable operation in emergencies.
5. Structural Design and Building Load-Bearing Requirements
Load-Bearing Design of Elevator Shaft
Ensure that the elevator shaft can support the weight of the elevator equipment, including the elevator car, counterweight, traction machine, and other components.
Machine Room and Equipment Location
Design the location and layout of the elevator machine room to ensure that the elevator equipment (e.g., control cabinets, drive equipment) can be smoothly installed and meet maintenance requirements.
6. Energy Saving and Environmental Protection Design
Elevator Energy-Saving Plan
Select an elevator system with energy recovery functions (e.g., regenerative braking technology) to reduce energy consumption.
Optimize Elevator Design
Reduce energy consumption and ensure the overall energy efficiency of the building by optimizing the number of elevators, dispatching system, and shaft space.
7. Construction and Installation
Purchase and Installation Plan for High-Rise Elevator Equipment
Identify the elevator equipment supplier and construction team, and coordinate the purchasing, transportation, and installation of the equipment.
Coordinate Elevator Installation and Construction
Ensure proper coordination between the construction of the elevator shaft, machine room, and other components, aligning the installation schedule to avoid conflicts during construction.
8. Testing and Acceptance
Elevator System Commissioning
After installation, conduct load tests, operational tests, and speed tests to ensure the elevator operates smoothly.
Safety Acceptance and Functional Testing
Verify that the elevator’s safety systems (e.g., emergency braking, emergency stop, fire protection) are functioning properly and compliant with all building regulations and safety standards.
9. Maintenance and Post-Management
Regular Inspection and Maintenance
To ensure the long-term safe operation of the elevator, regular inspections and maintenance should be scheduled, especially before peak usage periods.
Elevator System Upgrades and Optimization
As the building ages, regularly evaluate the elevator system’s performance and upgrade or optimize the system based on actual usage needs.
Classic Cases of High-Rise Elevators
Burj Khalifa (Dubai, UAE)
The use of double-decker elevators and shuttle elevator systems ensures the efficient operation of this super high-rise building, quickly addressing large passenger flows and ensuring smooth operation during peak hours.
Petronas Twin Towers (Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia)
The Petronas Twin Towers improve elevator efficiency through shared shaft design, reducing the core space occupied by elevators and optimizing space utilization.
Empire State Building (New York, USA)
After modernization, the Empire State Building’s elevator system significantly improved capacity and energy savings, solving the elevator congestion issue during peak hours.
Conclusion
High-rise elevator planning is not only about vertical transportation, but also an important part of building design. By applying reasonable zoning planning, intelligent scheduling systems and energy-saving technologies, the building’s operational efficiency, user comfort and energy performance can be significantly improved. The strategies and technologies discussed in this article, such as double-decker elevators, machine room-less elevators and traffic flow analysis, can guide your decision-making. For more complex needs, please contact our professional team to customize the elevator system: [BDFUJI Custom Elevator Solutions].
FAQs
How to choose a suitable elevator system for super high-rise buildings?
When choosing an elevator system for super high-rise buildings, consider the building’s height, expected passenger flow, and usage frequency. High-speed elevators are essential for providing faster vertical transportation and reducing waiting times. Additionally, machine room-less elevators (MRLs) save space while improving energy efficiency. Intelligent control systems, such as destination control systems, should also be considered to optimize elevator dispatch and minimize congestion during peak hours.
In high-rise buildings, how can we reduce energy consumption through elevator systems?
The key to reducing energy consumption is selecting an efficient and energy-saving elevator system. MRLs and variable frequency drive (VFD) systems significantly lower energy usage. The design of MRLs saves space and enhances efficiency by eliminating the need for traditional machine rooms. Energy recovery systems are crucial, as they can capture and reuse energy during the descent. Furthermore, intelligent scheduling systems and destination control systems optimize elevator dispatch, reducing unnecessary empty car movements and further cutting energy consumption.
What are the advantages of double-decker elevator systems in high-rise buildings?
Double-decker elevator systems serve two adjacent floors at once, improving transportation efficiency. They reduce the number of stops, making elevators more efficient, especially in high-frequency, high-traffic environments. These elevators increase passenger capacity, optimize shaft use, and reduce the occupation of building core space. Double-decker elevators are ideal for large commercial complexes and office buildings with dense traffic, effectively addressing elevator congestion during peak hours.
How to design an elevator dispatching system suitable for peak hours?
During peak hours, the dispatch system must be efficient and intelligent. The destination control system is key to improving dispatch efficiency. It intelligently assigns elevators based on passengers’ destination floors, reducing unnecessary stops and shortening waiting times. The intelligent dispatch system can also adjust the elevator’s route according to real-time passenger flow, optimizing elevator use during peak hours. Together, these systems efficiently manage passenger flow and improve overall operational efficiency.
How can ropeless elevators overcome the limitations of traditional systems and be suitable for super high-rise buildings?
Ropeless elevators (e.g., maglev elevators) break the vertical-only movement limitation by using magnetic levitation technology. This system enables elevators to move horizontally as well as vertically, allowing for more flexible designs in super high-rise buildings. Ropeless elevators reduce space requirements for traditional elevator shafts, offering more architectural flexibility. Additionally, they provide higher transportation efficiency and faster response times, making vertical transportation in super high-rise buildings more efficient.