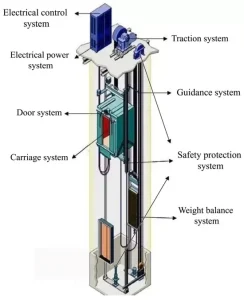
Tasks that used to take a lot of time or effort—like climbing many stairs or moving heavy goods—are now much easier thanks to elevators. Elevators are machines that help people and items move safely between floors in a building.
There are different types of elevators. Each type of elevator is made for a certain kind of building or job. These include hydraulic elevators, traction elevators, machine-room-less elevators, vacuum elevators, and screw elevators. Hydraulic elevators use fluid pressure to lift the cab and are great for short buildings. Traction elevators use ropes and motors to move faster and higher, making them ideal for tall buildings. Vacuum elevators use air pressure and are popular in homes because they are compact and easy to install.
If you want to understand how elevators work and which type is best for your space, keep reading. In this guide, we’ll explain the most common types of elevators, how they work, and where they are used.
Elevator Classification Method
Elevators come in different types, and each type is designed for a specific purpose. The way we classify elevators depends on different factors. These factors help us choose the best elevator for our needs. Below are the most common ways to classify elevators and their explanations:
1. By Purpose
This method sorts elevators based on what they are used for.
For example, passenger elevators are for people, while freight elevators are for carrying goods.
2. By Drive Type
This classification looks at how the elevator moves.
Some elevators use hydraulic systems (using fluid pressure), others use cables and motors (like traction elevators), and some use air pressure (like vacuum elevators).
3. By Speed
Elevators can also be classified by how fast they go.
Low-speed elevators are used for shorter buildings, while high-speed elevators are used in tall buildings to move people quickly.
4. By Load Capacity
This method divides elevators by how much weight they can carry.
Light-duty elevators carry fewer people or smaller loads, while heavy-duty elevators can carry bigger loads or more people.
5. By Installation Type
This classification is based on how the elevator is installed in a building.
Some elevators need a special room to store the machinery (machine-room elevator), while others don’t need this room (machine-room-less elevator).
Main Types of Elevators
When choosing a lift for a building, people use different types of elevators based on how tall the building is, how often the elevator will be used, and how much space is available. These include:
Hydraulic Elevators
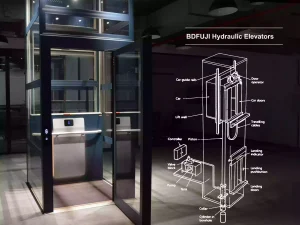
Hydraulic elevators use liquid pressure to move the elevator up and down. A piston pushes the elevator car from below.
This type is common in short buildings. It is smooth and not too expensive to install, but it moves slowly and needs extra space for the machine.
Traction Elevators
Traction elevators use steel ropes and a motor to move the car. A heavy counterweight helps lift the car.
This type is good for tall buildings. It is faster and uses less energy, but it costs more and needs strong support in the building.
Machine-Room-Less (MRL) Elevators
MRL elevators are a type of traction elevator. They do not need a machine room because the motor fits inside the shaft. This saves space.
MRL elevators are often used in buildings that don’t have much extra room. They are modern and energy-efficient, but harder to fix when something goes wrong.
Vacuum Elevators
Vacuum elevators use air pressure to lift and lower the car inside a tube. They do not need a big pit or machine room.
These are often used in homes. They are quiet, safe, and easy to install, but they move slowly and carry fewer people.
Screw-Driven Elevators
Screw-Driven Elevators use a long turning screw to raise the car. As the screw turns, the car goes up or down.
These elevators are small, safe, and good for houses. They don’t go very fast, and they can’t carry very heavy loads.
Other Classification Methods
Besides the main types, elevators can also be grouped in other ways.
| By Use | By Speed | By Load Capacity | By Installation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Passenger Elevator | Low Speed (under 200 ft/min) | Light Load (under 1,000 lbs) | With Pit and Machine Room |
| Freight Elevator | Medium Speed (200–500 ft/min) | Standard Load (1,000–5,000 lbs) | Pitless and Machine-Room-Less |
| Service Elevator | High Speed (over 500 ft/min) | Heavy Load (over 5,000 lbs) | Machine Room Inside Shaft |
| Dumbwaiter | Outdoor or Shaft-Less Design |
Applications of Different Elevator Types
Residential Buildings
For homes and apartment buildings, the best types of elevators are hydraulic elevators, screw elevators, and vacuum elevators. These elevators are small, quiet, and good for low to mid-rise buildings.
These types of elevators are great for residential use because they do not need much space and are easy to install. They are also safe and simple to use for seniors, children, or people with disabilities.
You can find home elevators in tall apartment buildings, townhouses, and even private homes. They help people carry groceries, luggage, or laundry between floors without using stairs.
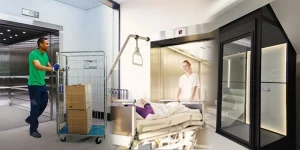
Hospitals
In hospitals, the most useful types of elevators are large traction elevators and hydraulic elevators. These elevators are wide, smooth, and strong enough to carry beds and medical equipment.
These types of elevators work well in hospitals because they can move patients safely and quickly. They are also quiet and gentle, which is important for sick or injured people.
You can find these elevators in emergency rooms, surgery wings, and patient care areas. They carry patients, doctors, stretchers, and machines between different hospital floors.
Retail Stores and Malls
For shopping malls and big stores, the best types of elevators are machine-room-less elevators and hydraulic elevators. These elevators are safe, easy to use, and good for carrying shoppers and carts.
These types of elevators are helpful because people in malls often carry bags, strollers, or wheelchairs. They also help store workers move products between storage and sales areas.
You can find these elevators in department stores, fashion malls, supermarkets, and outlets. They make shopping more comfortable for everyone.
Warehouses and Factories
For industrial areas, the strongest types of elevators are freight elevators and traction elevators. These elevators are built to carry very heavy loads, like boxes, tools, or machines.
These types of elevators are important because workers need to move large or heavy items between floors. They save time and help keep the workplace safe.
You can find freight elevators in warehouses, factories, and shipping centers. They move pallets, crates, and even small forklifts from one level to another.
How to Choose the Best Elevator Type
The best elevator type is chosen by understanding how the elevator will be used and what kind of building it will be in. You should think about the number of floors, how often it will be used, the people or items it will carry, and the space and power you have.
The structure of the building matters. A short building with only a few floors can use screw, vacuum, or hydraulic elevators. These elevators are good for homes or small offices. For taller buildings, traction elevators are better because they move faster and can go higher.
You also need to think about the size of the elevator. The elevator car should be big enough for the largest thing it will carry. A home elevator might only need to carry two people. A hospital elevator must carry beds and medical equipment. A freight elevator needs to carry large goods or heavy boxes.
How often the elevator is used is another key factor. In a busy office or apartment building, the elevator will run many times each day. For this, a strong and fast elevator like a traction model is a good choice. For light use, like in a house, a slower type is enough.
Power needs should also be checked. Some elevators, like hydraulic ones, use more energy. Others, like traction or vacuum elevators, use less. Before you install the elevator, make sure the power system in your building can handle it.
It is also important to think about repairs. All machines wear down over time. Choose an elevator brand that has easy-to-find spare parts. This makes it easier and faster to fix problems when they happen.
The cost of the elevator also matters. Some types cost less to buy and install, like screw or hydraulic elevators. Others cost more at the start but use less energy and last longer, like traction elevators.
Recommended Reading:
Traction Elevator vs Hydraulic Elevator: How to choose?
Conclusion
From quiet homes to busy city buildings, elevators are now part of everyday life. Understanding the different types of elevators helps you choose the right one for your space, your needs, and your budget.
If you are looking for a trusted elevator partner, BDFUJI Elevator is here to help. Since 2011, we have focused on creating high-quality elevators and escalators using advanced technology from Japan and Germany. With a production capacity of 50,000 units per year and a 160-meter test tower, we offer reliable products for homes, offices, hotels, shopping centers, and public transport systems.
No matter what your project needs, BDFUJI has the experience, equipment, and service team to support you. Contact us to learn more about our solutions or to speak with one of our elevator experts today.
Recommended Reading:
Outdoor Residential Elevator Type Inventory: Which One is Best for You?
6 Residential Elevator Types: Find the Right One for You
Elevator FAQ
The most commonly used types of elevators are traction elevators and hydraulic elevators. Traction elevators are often used in tall office or apartment buildings because they are fast and energy-efficient. Hydraulic elevators are common in low-rise buildings because they are simple and cost less to install.
For homes or small apartment buildings, good options include vacuum elevators, screw elevators, and small hydraulic elevators. These types are quiet, compact, and safe. They also work well in places with limited space.
What type of elevators are suitable for high-rise buildings?
Traction elevators are the best choice for high-rise buildings. They can move quickly between many floors and carry more people or weight. They are also more energy-efficient over long distances than other elevator types.