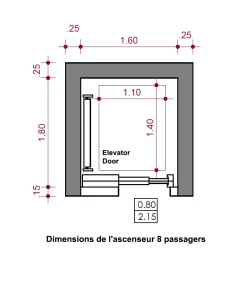
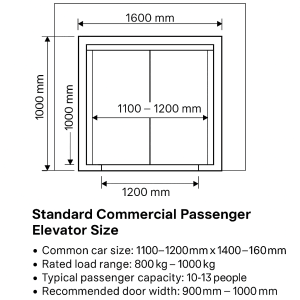
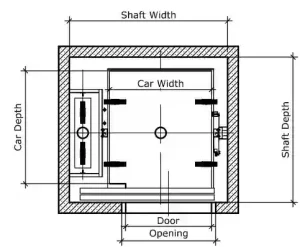
The design of the elevator shaft size is a critical aspect of building design, involving the coordination and responsibility allocation among multiple parties. In short, the planning of the elevator shaft size is a joint responsibility shared by architects, structural engineers, elevator manufacturers, and construction contractors. Close cooperation and clear responsibilities among all parties ensure that the elevator shaft design meets safety specifications, functional requirements, and building standards.
Basic Requirements for Elevator Shaft Size
The elevator shaft is a vertical space used to house the elevator machine room, car, and associated systems. Planning the size of the elevator shaft involves several key factors, which must be considered based on specific conditions such as elevator type, load requirements, and building height.
We can first understand what is the elevator shaft size through the following video content:
Below are the common dimensions of elevator shafts:
Width:
Standard Size: The width of the elevator shaft primarily depends on the size of the elevator car and whether it needs to accommodate the counterweight. For conventional passenger elevators, the width is usually between 2.5 meters and 3 meters; for larger freight or sightseeing elevators, the width may need to be more than 4 meters.
Calculation Basis: The width must provide enough space for both the car and counterweight to move while also considering equipment maintenance needs.
Depth:
Standard Size: The depth is determined by the vertical movement space needed for the elevator car and counterweight. For typical elevators, the depth of the elevator shaft generally ranges from 2.5 meters to 4 meters. For freight elevators, the depth may need to be 5 meters or more to accommodate larger items.
Considerations: The depth must account for the installation requirements of the elevator equipment and the movement space required to ensure that the system operates smoothly.
Height:
Standard Size: The height of the elevator shaft must meet the maximum travel requirements of the elevator. Generally, the height design of the shaft should cover the entire floor height and include a safety space of 0.3 meters to 0.5 meters to accommodate the full range of elevator movement.
Special Cases: For super high-rise buildings or special elevator types (such as ropeless elevators), the shaft height may need to be adjusted to allow for more space.
Pit Depth:
Standard Size: The pit depth ensures that the elevator system operates smoothly and accommodates the bottom installation requirements of the equipment. For standard elevators, the pit depth is usually designed to be between 1.5 meters and 2 meters. For heavy freight elevators or elevators in high-rise buildings, the pit depth may need to exceed 2.5 meters.
Considerations: The pit depth affects not only the elevator’s operation but also the ease of equipment maintenance and installation.
Door Opening Size:
Standard Size: The door opening size of the elevator shaft must match the type and opening mechanism of the elevator door. Common door opening sizes range from 0.9 meters (single door) to 1.6 meters (double door), with the exact size determined by the elevator’s load capacity and function. The door opening must allow for smooth entry and exit while meeting requirements for crowd flow and emergency evacuation.
Building Codes and Standards for Elevator Shafts
Elevator shaft design must adhere to multiple building codes and safety standards to ensure the elevator system’s stability and safety:
International Building Code (IBC)
The IBC provides clear requirements for elevator shaft dimensions and safety. It specifies the door opening size, shaft width, and height to ensure smooth installation of elevator equipment while meeting safety standards. For example, the IBC mandates that the width of the elevator shaft should be at least 2.5 meters for passenger elevators, and the height should accommodate elevator travel and building floors.
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
The ADA ensures that elevator shaft design takes into account the needs of individuals with disabilities, ensuring accessibility. Key ADA requirements include: the width of the elevator door opening must be at least 0.9 meters, and the interior of the elevator car must be spacious enough to accommodate assistive devices like wheelchairs. Additionally, the design of the elevator door opening and button height must meet barrier-free requirements.
ASME A17.1 Elevator Safety Code
The ASME A17.1 Safety Code sets detailed safety standards for the design, installation, and operation of elevator systems. It specifies shaft size, clearance distance, emergency passageways, and load capacity standards. The elevator shaft must meet installation requirements for elevator equipment, and its height and width must be adjusted based on the type of elevator (e.g., passenger or freight elevator). ASME A17.1 also mandates sufficient safety space in the elevator shaft to handle potential emergencies during operation.
The Impact of Different Types of Elevators on Shaft Size
The type of elevator significantly influences the requirements for shaft size. Here are the specific requirements for various common elevator types:
Passenger Elevator
Passenger elevator designs focus on space-saving and efficient transportation. Typically, the shaft width ranges from 2.5 meters to 3 meters, and the depth is between 2.5 meters and 4 meters. For smaller buildings (e.g., residential buildings), the shaft size may be smaller, but it must still meet safety and functional requirements.
Freight Elevator
Freight elevator designs focus more on accommodating large quantities of goods. Typically, the elevator shaft for a freight elevator is larger than that of a passenger elevator, often 3 meters to 4 meters wide, and the depth may range from 4 meters to 5 meters to accommodate larger items and shelves.
Service Elevator
The design of service elevators is similar to freight elevators but is typically used in smaller shopping malls, hospitals, and other locations. The shaft size may be around 2.5 meters wide and 3 meters deep.
Observation Elevator
Observation elevators, typically designed as transparent glass elevators to provide a scenic view, will have shaft sizes adjusted according to the building’s appearance and structural requirements. These shafts are generally larger than 3 meters.
Design Responsibility for Elevator Shaft Size
Architect
The architect is responsible for the overall design of the elevator shaft, including its location, layout, and preliminary dimensions. Architects consider the functional and aesthetic impact of the elevator shaft on the building and ensure it meets layout and regulatory requirements. They also coordinate with elevator manufacturers, structural engineers, and contractors to ensure the design is feasible.
Structural Engineer
Structural engineers ensure that the elevator shaft design meets safety standards and can support the weight of the elevator equipment and external forces (e.g., earthquake loads). They calculate the load-bearing capacity of the shaft and ensure the design of the shaft, pit, and top space meets the requirements for the elevator system.
Elevator Manufacturer
Elevator manufacturers provide technical specifications and dimensional requirements for the elevator equipment. Based on the model and performance requirements, manufacturers guide the design team in determining specific shaft parameters, such as width, depth, and door opening size. They also ensure the compatibility of the elevator equipment with the building’s structure for smooth installation and operation.
Construction Contractor
The construction contractor is responsible for constructing the elevator shaft according to the design specifications. They ensure accurate dimensions during the construction process and maintain the quality of construction to meet the design and building standards. The quality of the contractor’s work directly affects the safety and functionality of the elevator shaft.
Design Coordination Team
The design coordination team integrates the design requirements of all parties involved, resolving conflicts to ensure smooth communication between architects, structural engineers, and elevator manufacturers. Their work is crucial for the seamless implementation of the elevator shaft design and to avoid project delays.
Elevator Shaft Size Design Process
- Requirements Collection and Preliminary Planning
The design team collects relevant requirements based on the building function, elevator type, and safety standards. The team will then develop a preliminary elevator shaft design plan to ensure it meets the building layout and elevator equipment installation needs. - Develop Size Specifications and Design Parameters
During the preliminary planning stage, the design team develops detailed size specifications for the elevator shaft based on elevator type, load requirements, and building specifications. These specifications include shaft width, depth, height, and other parameters to ensure smooth elevator installation and operation. - Coordinate Building Design with Elevator Manufacturer’s Specifications
The architect works closely with the elevator manufacturer to ensure the design of the elevator shaft aligns with technical requirements. The specifications provided by the manufacturer help the design team adjust shaft size for compatibility with the elevator equipment. - Structural Design and Safety Assessment
The structural engineer conducts an assessment to ensure the shaft’s load-bearing capacity meets safety standards. They also perform a safety assessment to ensure the elevator shaft can support the equipment’s weight and comply with seismic design specifications. - Design Review and Approval Process
Once the design is complete, all drawings undergo a review and approval process. The architect, structural engineer, and elevator manufacturer review the design to ensure it meets building specifications and safety standards. - Construction Drawing Preparation and On-site Coordination
After the design is approved, the construction team will implement the design. The construction drawings must detail all dimensions of the elevator shaft, and the construction team is responsible for ensuring accurate on-site execution according to the design.
FAQ
The Role and Responsibilities of Architects in Elevator Shaft Planning
Architects are responsible for planning the location and preliminary dimensions of the elevator shaft and coordinating with other parties to ensure the design meets building requirements.
Who is Responsible for Confirming Shaft Dimensions During Construction?
Dimension confirmation during construction is the responsibility of the construction contractor, but it must follow the design specifications and building codes.
The Role of Elevator Manufacturers in Shaft Dimensions
Elevator manufacturers provide specifications for the elevator equipment and ensure compatibility with the shaft design.
Conclusion
The planning of elevator shaft dimensions is primarily the architect’s responsibility. Architects determine the location and preliminary dimensions of the shaft based on the overall building design and functional requirements. However, the final dimensions are adjusted based on the equipment specifications provided by the elevator manufacturer to ensure compatibility. For smooth implementation, BDFUJI recommends early communication with the elevator manufacturer to ensure the elevator shaft design meets all technical requirements.